Surgery to Reduce the Breasts
Breast reduction or Reduction Mammaplasty, is a common plastic surgery procedure to help reduce excessively large breasts, in some extreme cases known as gigantomastia. These patients are often symptomatic suffering from neck, shoulder, and upper back pain as a result of the excess weight on the chest wall from the large breasts. Breast reduction alleviates such symptoms leaving patients free of pain and happy with their new breast size and shape.
Evaluation for Breast Reduction
Breast reduction is ideal for people with excessive and pendulous breasts with symptoms including neck, shoulder and back pain along with shoulder grooving (marks from bra on the shoulders).
What Attributes Make a Good Candidate for Breast Reduction?
- Good physical health with stable weight
- Nonsmoker
- Disproportionately large breast compared to their body
- Asymmetric breasts
- Back, shoulder, and/or neck pain caused by size and weight of breasts
- Trouble with sports and activity due to breast size
- Regular clothes do not fit properly
- Bra straps leave marks on shoulders and breasts/chest
Often, patients who undergo breast reduction may require revision or repeat reduction after pregnancy or with significant weight gain or loss.
Breast reduction surgery may be covered by your health insurance plan. This is based upon your insurance type in addition to certain criteria required based upon breast size and excess. This is something that Dr. Som’s team can help clarify.
When choosing a surgeon, look for a board-certified plastic surgeon, like Dr. Som. Also, remember that your level of comfort with him or her is just as important as the surgical cost.
“Great Surgeon, very empathetic, down to earth, humble and a great physician.
My mom had her breast reduction surgery, and was the best experience my mother ever had. He is nice and I highly recommend.”
What Breast Reduction Will Not Do
Breast reduction is not a substitute for exercise and traditional forms of weight loss. It is appropriate for reduction and reshaping of pendulous and excessively large breasts in those that have already attempted to have improvement with weight loss and do not have large breasts due to excess weight. Most people would recommend initial weight loss to optimal Body Mass Index (BMI) prior to breast reduction.
Procedure Steps
A breast reduction procedure includes the following steps:
Step 1 – Anesthesia
Medications through the IV and inhaled gases are administered during the surgical procedures to help keep patients comfortable and pain free during the surgery. This procedure requires general anesthesia.
Step 2 – Injections
The incision pattern is marked in the preoperative area before coming into the operating room. After anesthesia is induced we then start out by injection local anesthetic to help minimize postoperative pain, but also to help with the surgical reduction. Often times liposuction will be added to the procedure to help with debulking of the breast tissue that extends into the axilla (armpit region). This anesthetic solution makes this possible.
Step 3 – Incisions
There are several options for incisions based upon the amount of reduction and reshaping required to achieve the optimal shape. Additional criteria include size and shape of the areolas, degree of breast ptosis (sagging) and skin elasticity and quality in particular in relation with extra skin. The 3 incisions include:
- Peri-areolar: this involves an incision around the areola (pink area around the nipple) – at times can be accomplished with minimal to no scar
- Elliptical/Vertical: ellipse shaped pattern of lift surrounding the areola extending down along the length of the inferior aspect of the breast
- Wise pattern (anchor pattern): Incision around the areola with initial dome shape. Upon suturing closed, final pattern is that of an anchor with peri-areolar incision, vertical limb extending to inframammary fold with extension medially and laterally; this incision is used for more extensive lifts requiring more resection and reshaping
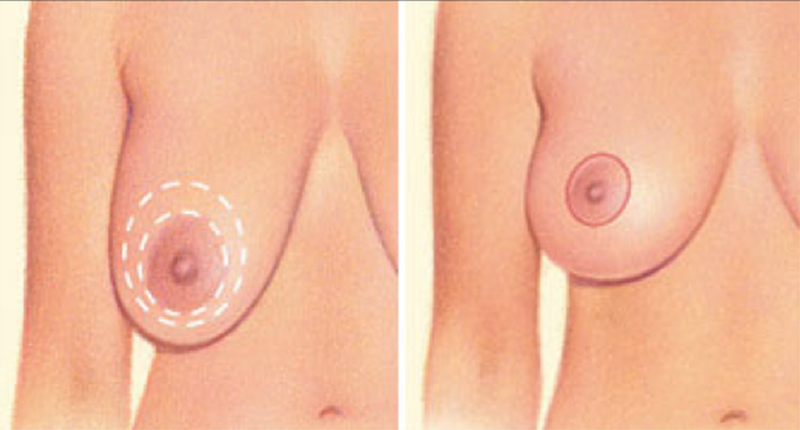
Peri-areolar (Around the areola)
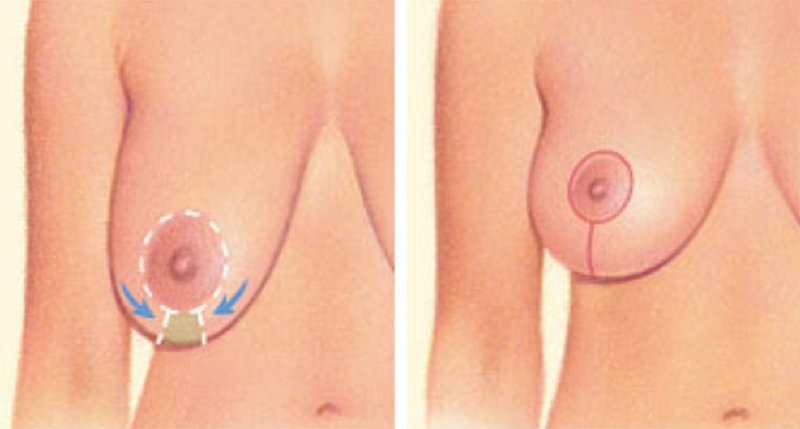
Elliptical or vertical (Around the areola and vertically down from the areola to the breast crease)
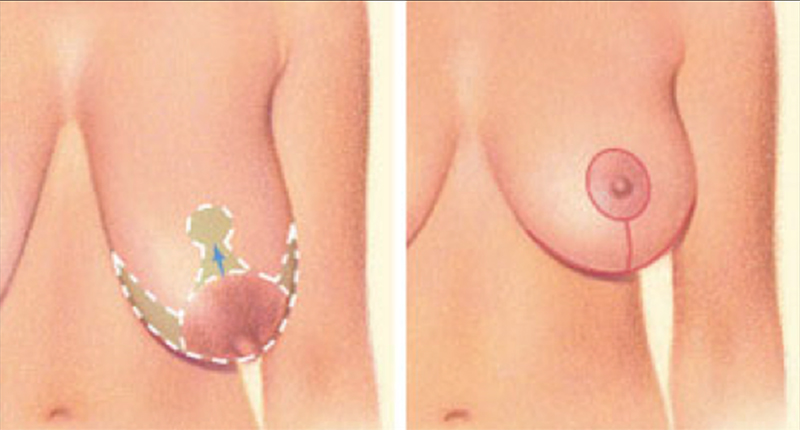
Wise pattern (Anchor pattern: Around the areola, vertically down and horizontally along the breast crease)
Step 4 – Reshaping Breasts
The excess breast skin is excised and reshaped based upon the initial markings. The premade keyhole pattern for the breast is used to re-approximate skin edges with a device to approximate the new nipple areolar position and shape. The nipple is brought into the new keyhole pattern and repositioned in its lifted position. Next, the inferior aspect of the breast tissue under the raised nipple-areolar complex is brought together to create support columns for the remaining breast tissue. The skin and soft tissue is closed.
Prior to completion of the closure, liposuction can be added if needed to help smooth out any irregularities or to reach excess tissue in the axilla.
Then special surgical tape is placed along the incisions to provide support for the closure and help maintain the newly reshaped breast. Lastly, the newly reshaped breasts are placed into special surgical bras to provide support and maintain shape of the new breasts.
Step 5 – Results
There is immediate improvement in symptoms including neck, shoulder and back pain; in addition, to the shoulder grooving caused by the straps of the bra. However, there is significant edema that will be presents for the first 6-12 weeks after which the breast shape will start to be apparent. It may often take 6-12 months for the final breast shape to present itself.
Although it takes several weeks for the shape to become evident, this procedure carries the highest satisfaction rate for patient’s that are truly symptomatic due to the immediate improvement of symptoms.
Risks and Safety
It is important to understand not only the procedure itself but also all the risks that come with any procedure. Once these are known then an appropriate decision can be made.
Risks include: anesthesia risks, bleeding, infection, fluid collection including seroma and hematoma formation, wound healing complications requiring prolonged wound care and healing, scar tissue formation, breast asymmetry and irregularities, cyst formation from fat necrosis, partial or complete nipple or areola loss, deep venous thrombosis or cardiac and pulmonary complications, and/or revisional surgery.
To learn more about breast reduction, what procedure may be right for you, please contact Dr. Som.